- What is WCF?
ü WCF stands
for Windows Communication Foundation (WCF).
ü This is
considered as the Microsoft Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) platform for
building distributed and interoperable applications.
ü WCF unifies
ASMX, Remoting, and Enterprise Services stacks and provides a single
programming model.
ü WCF
services are interoperable and supports all the core Web services
standards.
ü A WCF
service also provide extension points to quickly adapt to new protocols and
updates and integrates very easily with the earlier Microsoft technologies like
Enterprise Services, COM and MSMQ.
- Why should I use WCF?
ü WCF is
interoperable with other services when compared to .Net Remoting, where the
client and service have to be .Net.
ü WCF
services provide better reliability and security in compared to ASMX web
services.
ü In WCF,
there is no need to make much change in code for implementing the security
model and changing the binding. Small changes in the configuration will make
your requirements.
ü WCF has
integrated logging mechanism, changing the configuration file settings will
provide this functionality. In other technology developer has to write the code.
3. What is difference between WCF and Web Services?
ü Protocol: Web services
can only be invoked by HTTP (traditional web service with .asmx). While WCF
Service or a WCF component can be invoked by any protocol (like http, tcp etc.)
and any transport type.
ü Flexibility: web
services are not flexible. However, WCF Services are flexible. If you make a
new version of the service then you need to just expose a new end. Therefore,
services are agile and which is a very practical approach looking at the
current business trends.
ü Ease of Development: We develop
WCF as contracts, interface, operations, and data contracts. As the developer
we are more focused on the business logic services and need not worry about
channel stack. WCF is a unified programming API for any kind of services so we
create the service and use configuration information to set up the
communication mechanism like HTTP/TCP/MSMQ etc
ü XmlSerializer and DataContractSerializer
That
Web Services Use XmlSerializer But WCF Uses
DataContractSerializer which is better in Performance as Compared to XmlSerializer.
Key issues with XmlSerializer to serialize .NET types to XML
* Only Public fields or Properties of .NET types can be translated into XML.
* Only the classes which implement IEnumerable interface.
* Classes that implement the IDictionary interface, such as Hash table can not be serialized.
The DataContractAttribute can be applied to the class or a structure. DataMemberAttribute can be applied to field or a property and theses fields or properties can be either public or private. A practical benefit of the design of the DataContractSerializer is better performance over XmlSerializer.
DataContractSerializer which is better in Performance as Compared to XmlSerializer.
Key issues with XmlSerializer to serialize .NET types to XML
* Only Public fields or Properties of .NET types can be translated into XML.
* Only the classes which implement IEnumerable interface.
* Classes that implement the IDictionary interface, such as Hash table can not be serialized.
The DataContractAttribute can be applied to the class or a structure. DataMemberAttribute can be applied to field or a property and theses fields or properties can be either public or private. A practical benefit of the design of the DataContractSerializer is better performance over XmlSerializer.
- What is service and client in perspective of data
communication?
ü A
service is a unit of functionality exposed to the world.
The client of a service is merely the party consuming the service.
The client of a service is merely the party consuming the service.
- What is SOA Service?
ü SOA is
Service Oriented Architecture. SOA service is the encapsulation of a high level
business concept. A SOA service is composed of three parts.
Any
Service that fulfills above three requirements is SOA
- What are the core components of WCF?
ü Like
any other SOA Service the three core components of WCF are:
a.
A service class
b.
A hosting service
c.
Endpoints to expose the service
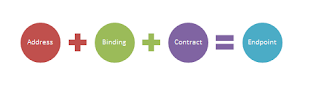
- What is ABC in WCF?
8.
What is
an endpoint?
ü WCF
Service is a program that exposes a collection of Endpoints. Each Endpoint is a
portal for communicating with the world.
ü All the
WCF communications are take place through end point. End point consists of
three components.
a.
Address
b.
Binding
c.
Contract
ü The
Endpoint is the fusion of Address, Contract and Binding.